wildwing 
WildWing: An open-source, autonomous and affordable UAS for animal behaviour video monitoring
This repo contains software to autonomously track group-living animals using Parrot Anafi drones.
Overview of WildWing framework
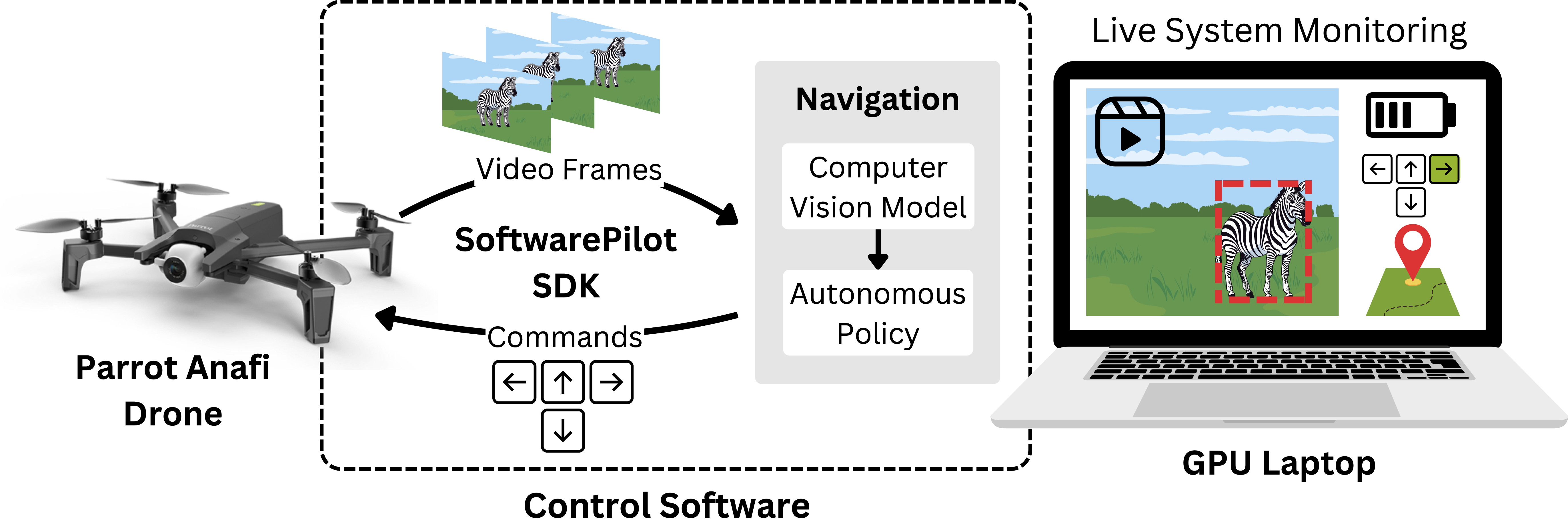 The WildWing Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) consists of three components: a Parrot Anafi drone, open-source control software, and a laptop equipped with GPU. The control software connects the drone to the autonomous navigation policy and allows users to monitor the system during deployment. The navigation policy analyzes video frames using computer vision models and determines the next commands to send to the drone. The control software is hosted on the laptop, where the users can also monitor the live WildWing system deployment.
The WildWing Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) consists of three components: a Parrot Anafi drone, open-source control software, and a laptop equipped with GPU. The control software connects the drone to the autonomous navigation policy and allows users to monitor the system during deployment. The navigation policy analyzes video frames using computer vision models and determines the next commands to send to the drone. The control software is hosted on the laptop, where the users can also monitor the live WildWing system deployment.
Paper and Dataset
Read our paper here and find dataset here.
Instructions for use
See the WildWing wiki for detailed instructions on how to deploy the WildWing system.
Hardware Requirements
This tool requires a Parrot Anafi drone and its controller, and a laptop running Ubuntu 22.04.4 OS on 86_64 architecture.
Software Requirements
This tool requires a laptop running Ubuntu 22.04.4 OS with VLC media player and a text editor, such as nano, emacs, or vi. VisualStudio Code may also be used.
See requirements.txt for required packages.
Details on the control software here: SoftwarePilot
Optional: SmartPhone with FreeFlight 6 app to connect drone and controller.
Step 1: Set-up hardware
- On the laptop, create conda environment using the requirements.txt file by running the following command. Note: you only need to create this conda environment once.
conda create --name wildwing --file requirements.txt - Connect drone and controller. Power on the drone and the Parrot Skycontroller. Plug the drone and the controller together with an USB-A (controller) to USB-C (drone) cable. The LED light on the controller will turn blue once connected and you can unplug the controller from the drone. Optional: you may also follow the instructions in the FreeFlight app to connect the drone and controller.
- Plug the controller into the laptop using USB-C cable.
- Using VLC media player, connect to drone live-stream. From the “Media” menu of VLC, select “Open network stream”. Enter “rtsp://192.168.53.1/live” in the Network URL field.
Step 2: Initialize software parameters
Initialize the following parameters in the python scripts. You can use these parameters to customize the mission for specific weather conditions, species, and habitats.
- controller.py
- DURATION: number of sections to execute autonomous tracking mission
- navigation.py
- x_dist: move +/- X meters in forward/backward plane
- x_dist_no_subject: move +/- X meters forward if no subject detected
- y_dist: move +/- X meters in left/right plane
- z_dist: move +/- X meters in up/down plane
Step 3: Launch drone
- Place drone in an area that is clear of obstructions
- Execute launch.sh from the command line. This will launch the drone, and initialize the log and telemetry files to record the mission data.
./launch.sh - Optional: manually maneuver from to a higher altitude using hand-held controller
Step 3: Monitor the system
- Monitor the drone’s PoV using the VLC livestream
- Monitor the YOLO model output and telemetry data in /missions/mission_record_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS/
- Check logs in /log/outputs_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS.log
Step 4: End mission
Once the mission duration is complete, you may continue the autonomous tracking mission, or land the drone using the remote controller. To continue the mission without first landing, comment out the takeoff line in controller.py, shown below, and save the file. Run launch.sh from the terminal to start the new mission.
# drone.piloting.takeoff()
Step 5: Analyze video data
This script saves the video recordings, telemetry data, and YOLO outputs for each mission. See the WildWing deployment data in Zenodo for example outputs.
To automatically label video data with behavior, we recommend using KABR tools.
To analyze the telemetry, use the data analysis notebook.
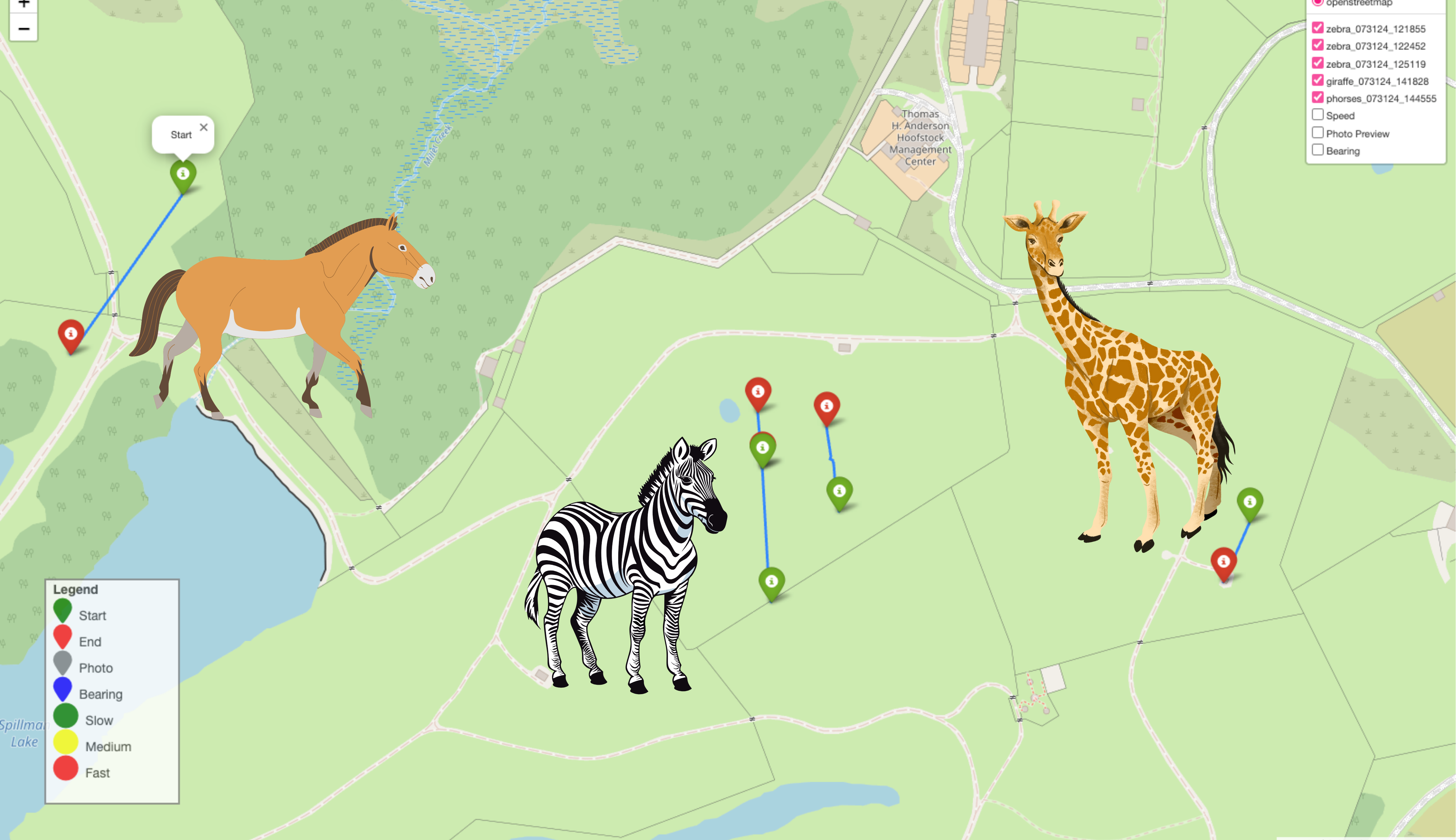 Mapped mission telemetry.
Mapped mission telemetry.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Imageomics Institute, which is funded by the US National Science Foundation’s Harnessing the Data Revolution (HDR) program under Award #2118240 (Imageomics: A New Frontier of Biological Information Powered by Knowledge-Guided Machine Learning). Additional support was also provided by the AI Institute for Intelligent Cyberinfrastructure with Computational Learning in the Environment (ICICLE), which is funded by the US National Science Foundation under Award #2112606. Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
The data was gathered at The Wilds, a private, non-profit conservation center located on nearly 10,000 acres of reclaimed coal mine land in southeastern Ohio. The Wilds is home to rare and endangered species from around the world living in natural, open-range habitats. The data collection was conducted under approval by the The Wilds Science Committee.